Environment
and
its Pollution
Air
- Composition of air is nitrogen 78.084% oxygen 20.946%. argon 0.934% carbon dioxide 0.033%.
- Region of air present around the earth is called atmosphere.
- Main layers from the surface of earth upwards
(a) Troposphere (b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere (d) Thermosphere.
- Most of atmospheric air is present in troposphere.
- Ozone layer present in the stratosphere region (at height of 32.50 km) protects the living being from harmful UV radiation coming from the sun.
- In 1775 French Scientist Lavoisier performed experiments on composition of air.
Air Pollution
- It is due to the presence of foreign substances in air. Main air pollutants are SO2,CO, nitrogen oxides, particulates etc.
Smog
(a) Classical smog It is formed in cool humid climate and is reducing in nature. It is also called London type smog.
(b) Photochemical smog It is formed in day time and is oxidizing in nature. It is also called Los Angeles smog.
Diseases Caused by Particulars
Disease Cause
Pneumoconiosis Coal dust
Silicosis Silica (from ceramics, glass and pottery industry)
Black lung disease Coal mines
White lung disease Textile industries
Asbestosis Asbestos
Byssinosis Cotton fiber dust
Green House Effect
- It is the heating up of earth and its objects due to trapping of outgoing IR radiations by green house gases like CO2, CH4No, O3 chlorofluorocarbon and water vapors.
Global Warming
- It is due to increased concentration of green house gases.
- It may lead to melting of ice caps and glaciers, spreading of several infectious diseases like malaria, sleeping sickness etc.
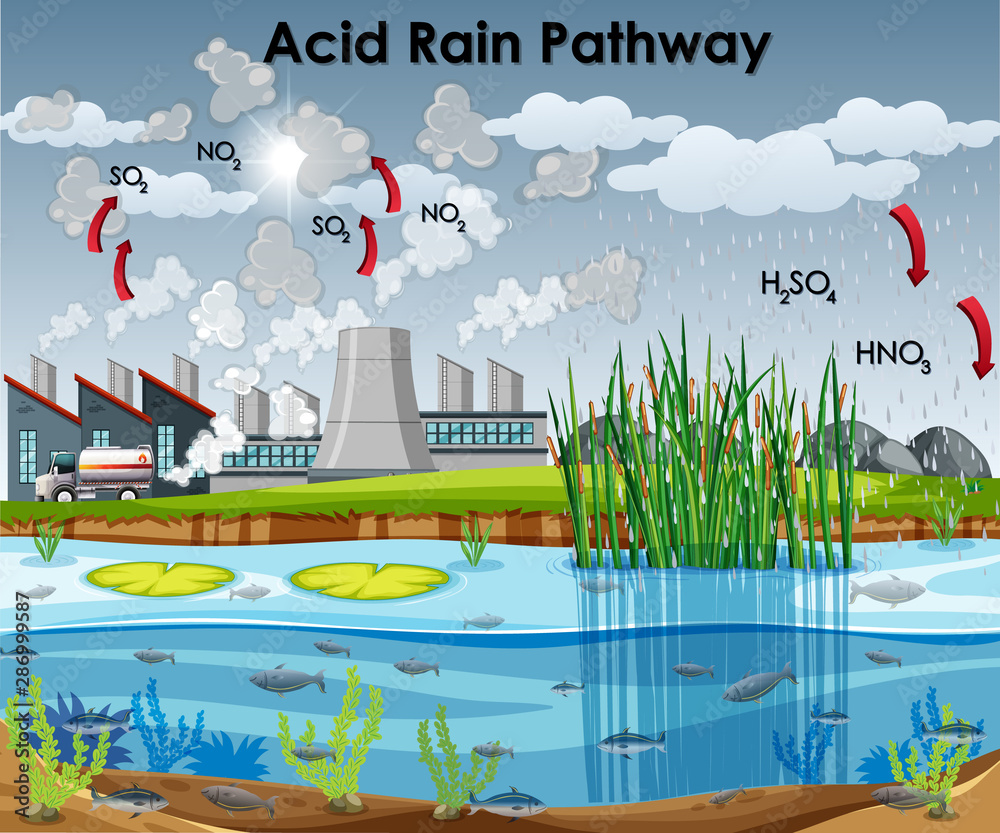
Acid Rain
- The pH of normal rain water is 5.6 due to the dissolution of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- When the pH of rain water is below 5, it is called acid rain (by Robert Augus).
- Acid rain damages the marble buildings (Taj Mahal) and monuments, corrodes metal pipes and results in several diseases.
- The main cause of acid rain is oxides of Sulphur and nitrogen. (H2SO4 and HNO3)
RIVERS AND DAMS FOR COMPETITIVE EXAMS
Water Pollution
- Cholera, dysentery, typhoid etc., are water borne diseases caused by bacteria.
- Mercury causes Mini mata disease, chromium and arsenic cause cancer and cadmium causes itai-itai disease.
- The usual effect of agricultural run off (due to the presence of nitrates and phosphates) is excessive algal growth in affected water DO is 5-6 and BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) is less than 5 ppm.